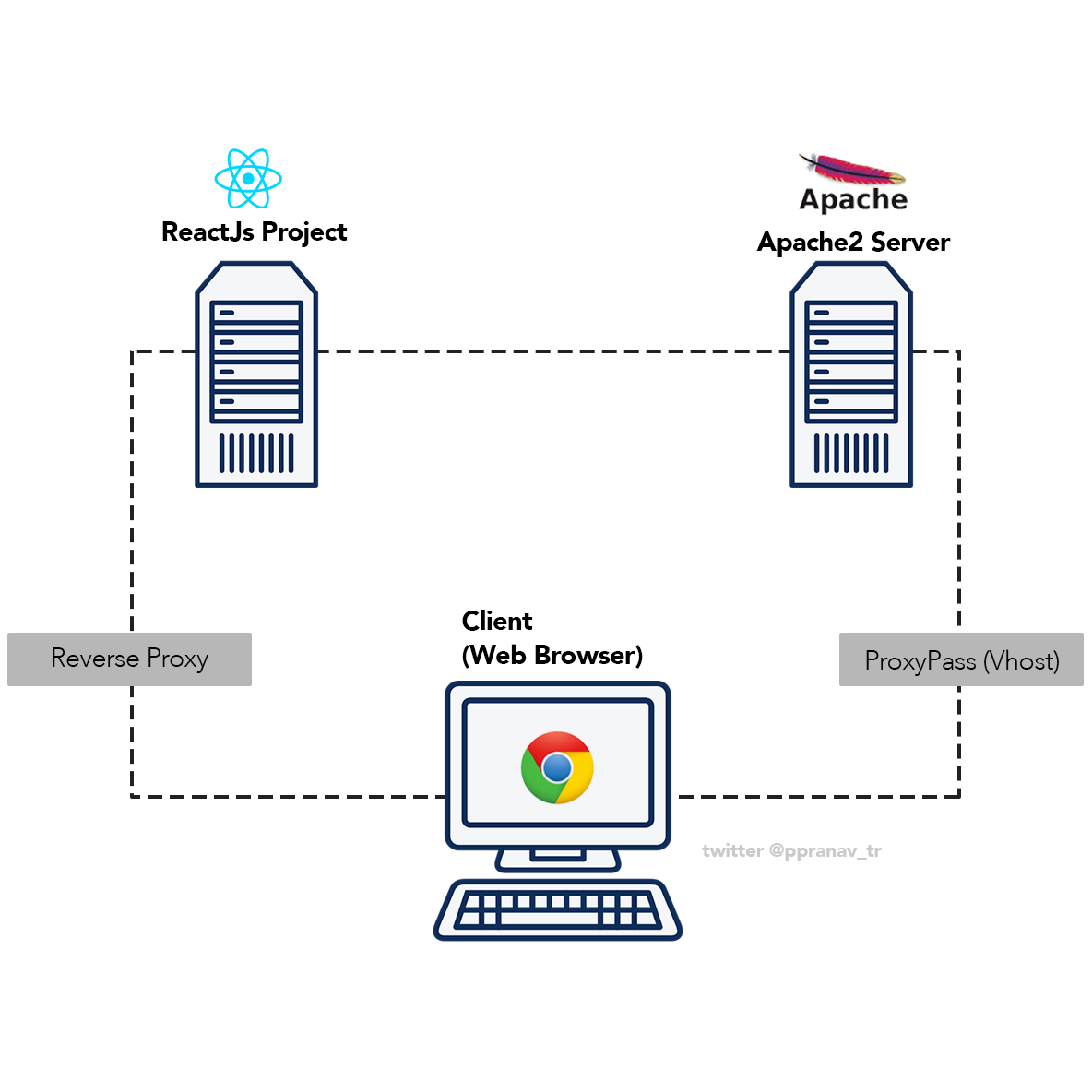
Buy cloud server sets the stage for a journey into the world of scalable and flexible hosting solutions. Cloud servers offer businesses and individuals a powerful alternative to traditional servers, providing enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability. This comprehensive guide explores the ins and outs of cloud servers, from understanding their core concepts to choosing the right provider and optimizing your setup for maximum efficiency.
We delve into the advantages of cloud servers, covering topics such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. We’ll guide you through the process of selecting the ideal cloud server for your specific needs, taking into account factors like pricing, performance, security, and support. From setting up and managing your cloud server to exploring future trends in cloud server technology, this guide equips you with the knowledge and insights to make informed decisions and harness the full potential of cloud computing.
Understanding Cloud Servers
Cloud servers are a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way businesses and individuals access and manage computing resources. They provide a flexible and scalable alternative to traditional servers, offering a wide range of benefits.
Cloud Server Features
Cloud servers are characterized by several key features that make them a compelling choice for various applications.
- Scalability: Cloud servers allow users to easily scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This means you can adjust your server capacity as your workload changes, ensuring optimal performance without the need for upfront investments in hardware.
- Flexibility: Cloud servers offer a wide range of configurations and options, enabling users to customize their environment to meet specific requirements. This flexibility extends to operating systems, software, and other components.
- Accessibility: Cloud servers are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This remote access makes it possible to manage and access your server resources from any location.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud servers can be more cost-effective than traditional servers, especially for businesses with fluctuating workloads. You only pay for the resources you use, reducing upfront capital expenditures and ongoing maintenance costs.
Comparison with Traditional Servers
Cloud servers differ significantly from traditional servers in several key aspects.
| Feature | Cloud Server | Traditional Server |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Data centers owned and operated by cloud providers | On-premises, within the user’s own facility |
| Ownership | Shared resources, owned and maintained by the cloud provider | Owned and maintained by the user |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, resources can be adjusted on demand | Limited scalability, requires physical hardware upgrades |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go model, based on usage | Significant upfront investment in hardware and maintenance |
| Management | Managed by the cloud provider, with user access to control panels | Managed by the user, requiring in-house expertise |
Types of Cloud Servers
Cloud servers come in various forms, each designed to meet different needs and requirements.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): VMs are software-based simulations of physical servers. They run on a shared physical server, providing users with a virtualized environment that mimics a dedicated server.
- Dedicated Servers: Dedicated servers provide users with a physical server that is dedicated exclusively to their use. This offers higher performance and security compared to VMs, but comes with a higher cost.
Benefits of Buying a Cloud Server
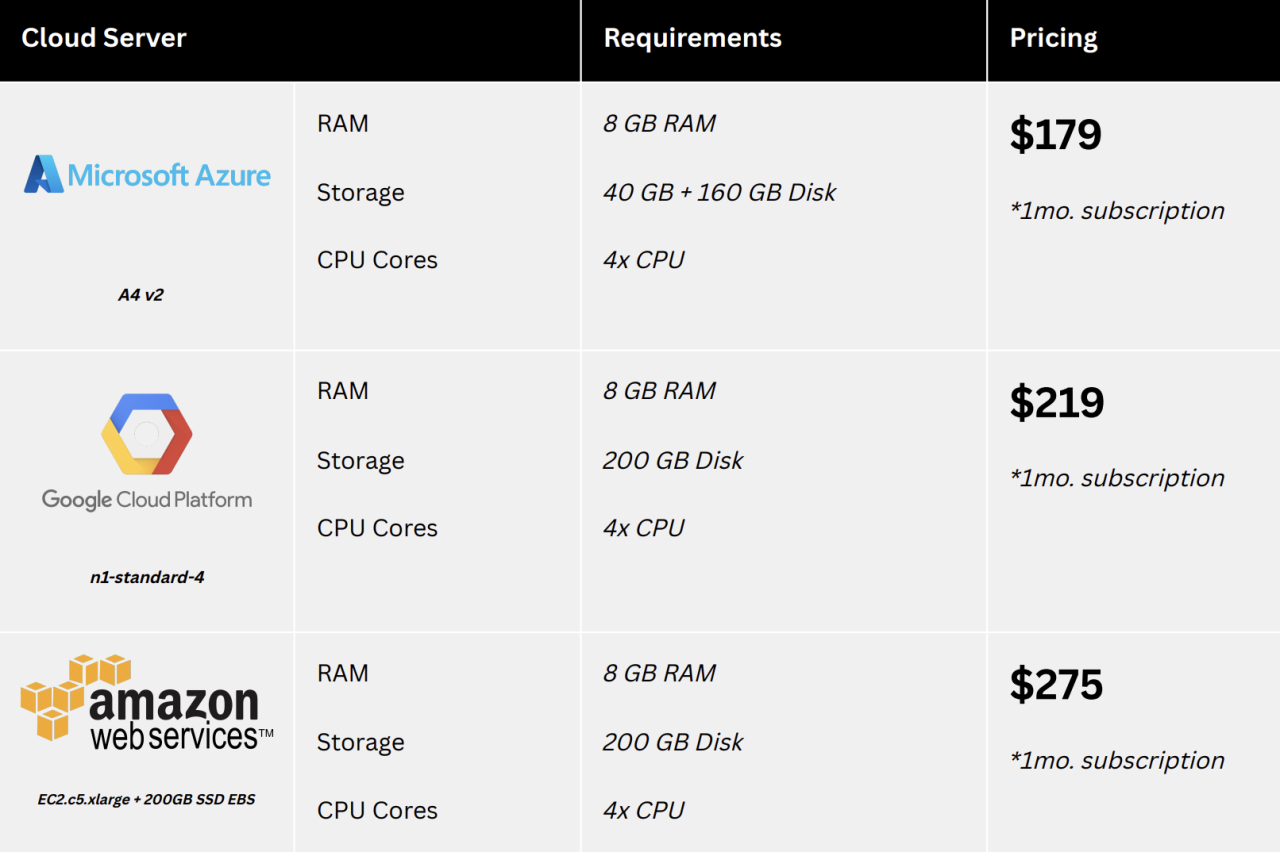
Cloud servers offer numerous advantages for businesses and individuals alike. Their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make them a compelling choice for various applications.
Scalability
Cloud servers provide the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This dynamic nature allows businesses to adapt to fluctuating workloads, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
“Scalability is the ability of a system, process, or organization to handle a growing amount of work.” – Wikipedia
- On-demand resource allocation: Cloud servers enable businesses to allocate resources like CPU, RAM, and storage as needed, avoiding unnecessary investments in hardware.
- Auto-scaling: Cloud platforms can automatically adjust resources based on predefined metrics, ensuring smooth operation during peak traffic or unexpected surges.
- Pay-as-you-go model: Businesses only pay for the resources they use, eliminating the need for upfront investments and reducing overall costs.
Flexibility
Cloud servers offer flexibility in terms of deployment, management, and customization. This allows businesses to tailor their infrastructure to specific requirements.
- Multiple operating systems and software: Cloud platforms support a wide range of operating systems and software applications, allowing businesses to choose the best fit for their needs.
- Rapid deployment: Cloud servers can be provisioned and deployed quickly, enabling businesses to launch new projects or services with minimal downtime.
- Easy management: Cloud platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and tools for managing servers, simplifying administration tasks and reducing IT overhead.
Cost-effectiveness, Buy cloud server
Cloud servers offer significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. This is achieved through reduced hardware investments, optimized resource utilization, and flexible payment models.
- Reduced capital expenditure (CAPEX): Businesses can avoid upfront investments in hardware, servers, and data centers, freeing up capital for other business needs.
- Lower operating expenses (OPEX): Cloud servers reduce ongoing costs associated with maintenance, power consumption, and IT staff.
- Predictable pricing: Cloud providers offer transparent pricing models, allowing businesses to budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs.
Factors to Consider When Buying a Cloud Server
Choosing the right cloud server provider is crucial for your business’s success. It involves evaluating various factors to ensure you get the best value for your investment and meet your specific needs.
Pricing
Cloud server pricing can vary significantly depending on the provider, the resources you require, and the duration of your contract. Understanding different pricing models is essential for making informed decisions.
- Pay-as-you-go: This model charges you only for the resources you use. It’s ideal for projects with fluctuating resource demands.
- Reserved instances: This model offers discounts for committing to a specific resource allocation for a set period. It’s suitable for predictable workloads with consistent resource needs.
- Spot instances: This model offers significant discounts for resources that are available at a particular time. It’s ideal for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
Performance
Performance is crucial for ensuring your cloud server can handle your workload efficiently. Several factors contribute to performance, including:
- CPU cores and memory: Higher core counts and more RAM provide better processing power and multitasking capabilities.
- Storage type and capacity: Choose storage options that align with your data needs, such as SSDs for high-performance applications or HDDs for cost-effective bulk storage.
- Network bandwidth and latency: Ensure sufficient bandwidth for fast data transfer and low latency for real-time applications.
Security
Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive data in the cloud.
- Data encryption: Ensure your provider offers data encryption both in transit and at rest.
- Access control: Implement strong access controls to limit unauthorized access to your server and data.
- Security features: Look for features like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability scanning to protect your server from threats.
Support
Reliable support is essential for resolving issues quickly and efficiently.
- Response time: Evaluate the provider’s response time for support requests.
- Availability: Ensure the provider offers support 24/7, especially if your applications require continuous uptime.
- Support channels: Look for providers that offer multiple support channels, such as phone, email, and live chat.
Comparing Cloud Server Providers
The following table compares the features and pricing of some popular cloud server providers:
| Provider | Pricing Model | CPU Cores | Memory | Storage | Security Features | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved instances, Spot instances | 1-96 vCPUs | 1-488 GiB | SSD, HDD, EBS | Encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection | 24/7 support, multiple channels |
| Microsoft Azure | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved instances | 1-128 vCPUs | 1-448 GiB | SSD, HDD, Azure Disk | Encryption, firewalls, security center | 24/7 support, multiple channels |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Pay-as-you-go, Sustained use discounts | 1-96 vCPUs | 1-488 GiB | SSD, HDD, Persistent Disk | Encryption, firewalls, security scanner | 24/7 support, multiple channels |
Choosing the Right Cloud Server for Your Needs
Selecting the right cloud server is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for your specific application. Understanding your application’s requirements and carefully considering the various factors involved in cloud server selection is essential.
Matching Cloud Server Configurations to Specific Use Cases
The configuration of a cloud server, including its processing power, memory, storage, and network bandwidth, directly influences its suitability for different applications. Here are examples of cloud server configurations suitable for various use cases:
- Websites: For basic websites with low traffic, a shared hosting solution might suffice. However, for high-traffic websites or those with demanding performance requirements, a cloud server with a dedicated CPU, ample RAM, and sufficient storage is recommended. For instance, a cloud server with 2 vCPUs, 4GB RAM, and 50GB SSD storage would be a suitable option for a medium-sized website.
- Databases: Databases require robust processing power, ample RAM, and fast storage to handle queries efficiently. For example, a cloud server with 4 vCPUs, 16GB RAM, and 200GB SSD storage would be suitable for a medium-sized database application. For larger databases or those with high transaction volumes, consider a cloud server with more processing power, memory, and storage.
- Gaming: Gaming applications demand high processing power, low latency, and sufficient bandwidth to provide a smooth and responsive gaming experience. A cloud server with a dedicated CPU, a high-speed network connection, and sufficient RAM would be ideal. For instance, a cloud server with 8 vCPUs, 32GB RAM, and a 1Gbps network connection would be suitable for a medium-sized gaming server.
Step-by-Step Guide for Choosing the Right Cloud Server
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right cloud server:
- Identify Your Application’s Requirements: Determine the specific needs of your application, including processing power, memory, storage, network bandwidth, and other factors.
- Estimate Traffic and Usage: Forecast the expected traffic and usage of your application. This will help you determine the required resources and server capacity.
- Consider Scalability and Flexibility: Choose a cloud server provider that offers scalability and flexibility, allowing you to easily adjust resources as your application’s needs evolve.
- Evaluate Pricing and Cost-Effectiveness: Compare pricing models and cost-effectiveness of different cloud server providers. Choose a provider that offers a balance between cost and performance.
- Explore Security Features: Assess the security features offered by different cloud server providers. Ensure the provider offers robust security measures to protect your data and applications.
- Check Support and Documentation: Evaluate the support and documentation offered by different cloud server providers. Choose a provider that offers comprehensive support and detailed documentation.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Selecting a Cloud Server
A flowchart can help visualize the decision-making process for selecting a cloud server:
- Start: Define your application’s requirements (processing power, memory, storage, etc.).
- Estimate Traffic and Usage: Determine expected traffic and usage patterns.
- Evaluate Scalability and Flexibility: Assess the provider’s ability to scale resources.
- Compare Pricing and Cost-Effectiveness: Analyze pricing models and cost-effectiveness.
- Assess Security Features: Check security measures offered by the provider.
- Evaluate Support and Documentation: Review support and documentation options.
- Select the Best Cloud Server: Choose the provider and server configuration that best meets your needs.
- End: You have successfully chosen the right cloud server for your application.
Buying a cloud server can provide the flexibility and scalability you need for your applications. If you’re looking for a way to securely connect your cloud server to industrial automation systems, consider implementing an OPC UA server. This protocol enables seamless data exchange between your server and industrial equipment, facilitating real-time monitoring and control.
With a cloud server and OPC UA integration, you can unlock a world of possibilities for your industrial operations.
Setting Up and Managing a Cloud Server
Setting up and managing a cloud server involves a series of steps that ensure your server is operational and secure. The process includes creating an account with a cloud provider, selecting a server configuration, and configuring security settings. Managing a cloud server involves tasks like installing software, monitoring performance, and troubleshooting issues.
Creating and Configuring a Cloud Server
Cloud server creation is straightforward, often involving a few clicks. Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer intuitive interfaces for creating and configuring servers. The process typically involves choosing a server type, specifying resources like RAM and storage, selecting an operating system, and defining network settings.
Accessing and Managing a Cloud Server Remotely
Accessing and managing a cloud server remotely is essential for administration and maintenance. Secure Shell (SSH) is a common protocol for accessing servers remotely, allowing you to execute commands and manage files. Cloud providers often provide web-based consoles for managing servers, offering features like monitoring, logging, and security configuration.
Common Server Management Tasks
Server management tasks include installing software, configuring security settings, and monitoring performance. Installing software involves downloading and installing applications using package managers or manual installation methods. Security configuration includes setting up firewalls, configuring user accounts, and implementing security patches. Monitoring server performance involves tracking resource usage, identifying potential bottlenecks, and addressing performance issues.
Security Considerations for Cloud Servers
In the world of cloud computing, security is paramount. Your cloud server houses your data, applications, and sensitive information, making it a prime target for malicious actors. Understanding the potential threats and implementing robust security measures is crucial to safeguarding your cloud environment.
Common Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Cloud servers are susceptible to various security threats, including:
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored on the cloud server, often through vulnerabilities in applications or misconfigured security settings.
- Malware infections: Malicious software can infect cloud servers, potentially stealing data, disrupting operations, or launching further attacks.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm a cloud server with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Misconfigurations: Incorrectly configured security settings, firewalls, or access controls can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Insider threats: Employees with access to the cloud server may intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
Best Practices for Securing a Cloud Server Environment
Here are some essential security practices to protect your cloud server:
- Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA): Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable MFA to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular security updates and patching: Keep your operating system, applications, and security software up-to-date to address known vulnerabilities.
- Secure network configuration: Use strong firewalls, network segmentation, and intrusion detection/prevention systems to protect your cloud server from unauthorized access.
- Data encryption: Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches.
- Regular security audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential threats.
- Implement a security information and event management (SIEM) system: A SIEM system can help you monitor your cloud server for suspicious activity and detect potential security incidents.
- Train your staff: Train your employees on best security practices, including password management, data security, and phishing awareness.
- Work with a reputable cloud provider: Choose a cloud provider with a strong security track record and robust security measures in place.
Cloud Server Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining a cloud server’s optimal performance and ensuring its reliability is crucial for smooth operations. Monitoring provides valuable insights into the server’s health and resource utilization, enabling proactive issue identification and timely intervention.
Monitoring Cloud Server Performance
Regularly monitoring cloud server performance helps identify potential issues before they impact operations. This allows for timely troubleshooting and prevents performance degradation.
- CPU Utilization: Monitoring CPU usage provides insight into the server’s workload. High CPU utilization can indicate resource constraints, potentially leading to performance bottlenecks.
- Memory Usage: Keeping track of memory consumption helps determine if the server has sufficient memory to handle current and future workloads. High memory utilization can result in slowdowns and system instability.
- Disk Space: Monitoring disk space usage helps ensure that there is enough space for the operating system, applications, and data. Insufficient disk space can lead to performance issues and data loss.
- Network Bandwidth: Tracking network bandwidth usage provides insight into the server’s network activity. High bandwidth utilization can indicate heavy traffic or potential network bottlenecks.
Common Monitoring Tools
Various tools can assist in monitoring cloud server performance. These tools provide real-time data, historical trends, and alerts for critical events.
- Cloud Provider Monitoring Tools: Most cloud providers offer built-in monitoring tools, providing insights into server performance, resource utilization, and network activity. These tools are often integrated with the cloud platform and provide comprehensive monitoring capabilities.
- Third-Party Monitoring Tools: Numerous third-party monitoring tools are available, offering advanced features and customization options. These tools can monitor various metrics, generate alerts, and provide detailed reports.
- Open-Source Monitoring Tools: Open-source monitoring tools provide cost-effective solutions with flexibility and customization. These tools offer a wide range of features and can be integrated with various cloud platforms.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal cloud server performance and stability.
- Software Updates: Keeping the operating system and applications up-to-date is crucial for security and performance. Regular updates address vulnerabilities and improve system stability.
- Security Patches: Applying security patches promptly is vital for protecting the server from known vulnerabilities. Security patches can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Disk Optimization: Regularly optimizing disk space by deleting unnecessary files and defragmenting the drive can improve performance. This ensures efficient disk utilization and prevents performance bottlenecks.
- Backup and Recovery: Regular backups are essential for protecting data from loss or corruption. Implementing a robust backup and recovery plan ensures data availability in case of unexpected events.
Cost Optimization for Cloud Servers
Optimizing cloud server costs is crucial for businesses of all sizes. While cloud computing offers flexibility and scalability, uncontrolled usage can lead to significant expenses. By implementing strategic cost optimization techniques, you can significantly reduce your cloud server bill without compromising performance.
Resource Optimization
Resource optimization involves using cloud resources efficiently and effectively to minimize unnecessary expenses.
- Right-sizing instances: Choose instances with the appropriate CPU, memory, and storage capacity for your workload. Overprovisioning can lead to wasted resources and higher costs. Regularly monitor your server performance and adjust instance sizes as needed.
- Auto-scaling: Configure auto-scaling to automatically adjust the number of instances based on demand. This ensures that you only pay for the resources you need, avoiding over-provisioning during peak periods and under-provisioning during low-demand periods.
- Spot instances: Leverage spot instances for non-critical workloads. Spot instances offer significant cost savings, but they can be terminated with short notice.
- Reserved instances: Consider reserved instances for predictable workloads. Reserved instances provide discounted pricing for a fixed period, offering cost savings for long-term commitments.
Efficient Usage
Efficient usage focuses on optimizing the way you use your cloud resources to reduce waste and unnecessary expenses.
- Idle server shutdown: Shut down servers when not in use, particularly during non-peak hours or weekends. This eliminates unnecessary costs associated with running idle servers.
- Storage optimization: Optimize storage usage by removing unnecessary data, compressing files, and using cost-effective storage tiers for different types of data.
- Network optimization: Minimize network traffic by optimizing your application code, using content delivery networks (CDNs), and optimizing database queries.
- Software optimization: Ensure that your applications are optimized for performance and efficiency. Regularly update software and libraries to benefit from performance enhancements.
Cost Optimization Techniques
The following table Artikels different cost optimization techniques and their potential benefits:
| Technique | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Right-sizing instances | Reduced instance costs by using only the resources you need. |
| Auto-scaling | Optimized instance utilization based on demand, reducing over-provisioning costs. |
| Spot instances | Significant cost savings for non-critical workloads. |
| Reserved instances | Discounted pricing for predictable workloads with long-term commitments. |
| Idle server shutdown | Eliminated costs associated with running idle servers. |
| Storage optimization | Reduced storage costs by removing unnecessary data and using cost-effective storage tiers. |
| Network optimization | Reduced network traffic costs through optimized application code and CDNs. |
| Software optimization | Improved performance and efficiency, leading to reduced resource usage. |
Future Trends in Cloud Server Technology: Buy Cloud Server
The cloud server landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user needs. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure for agility and scalability, new trends are emerging that will shape the future of cloud server technology.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud computing execution model where the cloud provider manages the server infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on writing and deploying code without worrying about server provisioning, scaling, or maintenance. This approach offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced operational overhead: Developers can focus on application logic rather than managing infrastructure.
- Scalability and elasticity: Serverless functions can automatically scale up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-per-use pricing models allow for cost optimization, as you only pay for the resources used.
Examples of serverless computing platforms include AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving performance for applications that require real-time processing. This approach is particularly beneficial for applications like:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Processing data from sensors and devices at the edge reduces network traffic and improves responsiveness.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): Edge computing enables low-latency rendering and interactive experiences.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs): Distributing content closer to users improves content delivery speed and reduces network congestion.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming cloud server technology, enabling intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making. Cloud servers are increasingly equipped with AI and ML capabilities, allowing for:
- Predictive maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze server performance data to predict potential failures and proactively address issues.
- Automated resource allocation: AI-powered systems can dynamically allocate resources based on real-time demand, optimizing server utilization.
- Security threat detection: AI algorithms can identify and mitigate security threats by analyzing network traffic and user behavior.
Cloud-Native Applications
Cloud-native applications are designed specifically for cloud environments, taking advantage of cloud services and architectures. These applications are typically built using microservices, containers, and DevOps practices, offering benefits like:
- Agility and scalability: Cloud-native applications can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demands.
- Improved resilience: Microservices architecture allows for independent deployment and scaling, enhancing fault tolerance.
- Faster development cycles: DevOps practices streamline development and deployment processes, enabling rapid iteration and innovation.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a rapidly evolving field that promises to revolutionize computing power. Cloud server providers are exploring the potential of quantum computing to solve complex problems that are intractable for traditional computers.
- Drug discovery: Quantum computers can simulate molecular interactions to accelerate drug development.
- Financial modeling: Quantum algorithms can optimize financial models and improve risk management.
- Materials science: Quantum computing can accelerate the discovery and development of new materials.
The Future of Cloud Servers
Cloud servers will continue to play a critical role in digital transformation, enabling businesses to leverage the power of cloud computing to innovate and grow. As technology advances, we can expect to see further development in areas like:
- Increased automation: Cloud server management will become increasingly automated, simplifying operations and reducing human error.
- Enhanced security: Cloud providers will continue to invest in advanced security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Greater sustainability: Cloud servers will become more energy-efficient, contributing to a greener IT landscape.
Final Thoughts
As you embark on your cloud server journey, remember that choosing the right provider and configuring your server for optimal performance are crucial for success. By understanding the benefits, factors to consider, and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can leverage the power of cloud servers to enhance your online presence, streamline operations, and drive growth. The future of cloud server technology is bright, with innovations like serverless computing and edge computing continuously pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Stay informed, embrace these advancements, and unlock the full potential of cloud computing for your business and personal endeavors.