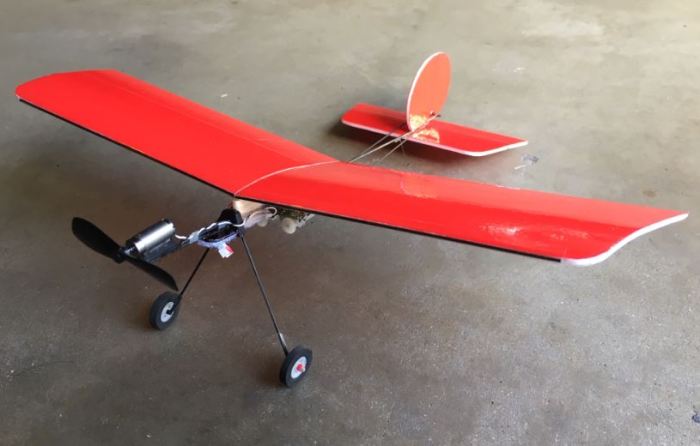
DIY RC airplane, a captivating realm where imagination takes flight, offers an unparalleled experience for hobbyists and aviation enthusiasts alike. Building your own RC airplane allows you to delve into the intricate world of aerodynamics, engineering, and electronics, culminating in the exhilarating joy of witnessing your creation soar through the skies.
From the initial design concept to the final assembly, the journey of constructing a DIY RC airplane is a rewarding one. It empowers you to customize every aspect of your aircraft, from its wingspan and airfoil to its power source and control systems. The satisfaction of seeing your meticulously crafted creation take to the air, responding to your commands with precision and grace, is truly unmatched.
Types of DIY RC Airplanes

Building your own RC airplane can be a rewarding experience, opening up a world of possibilities for flight enthusiasts. But with so many different types of RC airplanes, choosing the right one for your needs can be a daunting task. This guide will explore the various types of DIY RC airplanes based on their wing design and power source, highlighting their unique characteristics and flight capabilities.
Wing Design
The wing design of an RC airplane is a crucial factor determining its flight characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of some common wing designs:
- Wingspan: The wingspan refers to the distance between the wingtips. A larger wingspan generally provides greater stability and slower stall speeds, making the airplane more suitable for beginners. Smaller wingspans, on the other hand, offer increased maneuverability and agility, often found in sport and aerobatic airplanes.
- Airfoil: The airfoil is the cross-sectional shape of the wing. Different airfoil shapes generate different amounts of lift and drag, affecting the airplane’s performance. For instance, a symmetrical airfoil is often used in aerobatic airplanes, allowing for inverted flight, while a cambered airfoil is commonly found in gliders, maximizing lift for extended flight times.
- Dihedral: Dihedral refers to the upward angle of the wings relative to the fuselage. This angle contributes to stability, as it creates a restoring force that counteracts any rolling motion. A higher dihedral angle results in greater stability, often seen in beginner-friendly airplanes, while a lower dihedral angle allows for more aggressive maneuvers.
Power Source
The power source used to propel an RC airplane significantly influences its performance and operating characteristics. Here’s a look at the most common power sources:
- Electric: Electric-powered RC airplanes are becoming increasingly popular due to their simplicity, ease of maintenance, and relatively quiet operation. Electric motors are powered by batteries, which can be easily recharged. Electric airplanes offer excellent controllability and are suitable for various flight styles, from leisurely flying to aggressive aerobatics.
- Gasoline: Gasoline-powered RC airplanes provide more power and longer flight times compared to their electric counterparts. They typically use two-stroke engines, requiring a fuel mixture of gasoline and oil. While gasoline engines offer impressive power, they require more maintenance and can be louder than electric motors.
- Nitro: Nitro-powered RC airplanes are known for their high power output and quick acceleration. They use nitro-methane fuel, which burns hotter and faster than gasoline, resulting in impressive performance. However, nitro engines are more complex to maintain and require specialized tools and knowledge.
Electronics and Power Systems for DIY RC Airplanes
The heart of any RC airplane lies in its electronics and power system. This is what brings your model to life, enabling it to fly, maneuver, and respond to your commands. Understanding the different components and their roles is crucial for building a successful and enjoyable DIY RC airplane.
RC Receivers, Transmitters, and Servos
The communication between you and your RC airplane is made possible by a system of transmitters, receivers, and servos.
* Transmitters are the handheld devices you use to control your airplane. They send radio signals to the receiver.
* Receivers are the devices that receive the signals from the transmitter and translate them into instructions for the servos.
* Servos are small electric motors that receive instructions from the receiver and move control surfaces like ailerons, elevators, and rudders, enabling the airplane to fly.
These components work together to create a seamless control system for your airplane.
- Types of RC Receivers:
- Analog Receivers: These are older receivers that use analog signals for communication. They are generally cheaper but less reliable than digital receivers.
- Digital Receivers: These receivers use digital signals for communication, offering greater precision and responsiveness. They are also more resistant to interference.
- Types of RC Transmitters:
- 2.4 GHz Transmitters: These are the most common type of transmitter, offering long range and excellent interference resistance.
- 900 MHz Transmitters: These transmitters are less common but offer greater range and penetration through obstacles. They are also less susceptible to interference from other electronic devices.
- Types of Servos:
- Standard Servos: These are the most common type of servo, offering good performance at a reasonable price.
- Digital Servos: These servos use digital signals for communication, providing greater accuracy and speed. They are generally more expensive than standard servos.
- High-Torque Servos: These servos are designed for high-power applications, offering greater strength and power for larger airplanes.
Electric Motors, Batteries, and ESCs
The power system of your RC airplane consists of the electric motor, battery, and electronic speed controller (ESC).
* Electric Motors: These are the heart of your power system, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the propeller.
* Batteries: These provide the power to run the motor and other electronics.
* ESCs: These are electronic devices that control the speed and direction of the motor, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
- Selecting the Right Motor: The motor you choose will depend on the size and weight of your airplane, as well as the desired flight performance. Larger airplanes require more powerful motors, while smaller airplanes can get away with less powerful motors.
- KV Rating: This is a measure of the motor’s speed, expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM) per volt. A higher KV rating means a faster motor.
- Motor Size: The size of the motor is also important, as it determines the amount of power it can generate. Larger motors are generally more powerful.
- Selecting the Right Battery: The battery you choose will depend on the power requirements of your motor and the desired flight time.
- Battery Capacity: This is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) and indicates how much power the battery can store. A higher mAh rating means a longer flight time.
- Battery Voltage: This is measured in volts (V) and determines the amount of power the battery can deliver. Higher voltage batteries provide more power.
- Selecting the Right ESC: The ESC you choose must be compatible with the motor and battery you are using.
- Amperage Rating: The ESC’s amperage rating must be high enough to handle the current draw of the motor.
- Voltage Rating: The ESC’s voltage rating must be compatible with the battery you are using.
Wiring and Connections
Proper wiring and connections are crucial for the safety and functionality of your RC airplane.
Always use high-quality wires and connectors to ensure reliable connections.
- Battery Connection: Connect the battery to the ESC using the correct connectors. Ensure the polarity is correct, as connecting the battery in reverse can damage the ESC or motor.
- ESC Connection: Connect the ESC to the motor using the correct connectors. Again, ensure the polarity is correct.
- Receiver Connection: Connect the receiver to the ESC and servos using the correct connectors.
- Servos Connection: Connect the servos to the receiver using the correct connectors.
Advanced DIY RC Airplane Techniques

Taking your DIY RC airplane beyond basic flight requires delving into advanced techniques to customize and enhance performance. This section explores techniques for modifying your aircraft, implementing control systems, and integrating advanced features like landing gear, camera systems, and autopilot.
Customizing and Modifying DIY RC Airplanes
Customizing your DIY RC airplane can significantly enhance its performance and flight characteristics. You can modify various aspects, including the airframe, wing design, and power system.
- Airframe Modifications:
- Weight Reduction: Using lightweight materials like carbon fiber or balsa wood for the airframe can significantly reduce weight, improving maneuverability and flight time.
- Aerodynamic Improvements: Smoothing out the airframe by removing unnecessary protrusions and streamlining the fuselage can reduce drag and increase efficiency.
- Wing Modifications: Adjusting the wingspan, dihedral, and airfoil can impact the plane’s stability, lift, and maneuverability. Experimenting with different wing designs can significantly affect the flight characteristics.
- Power System Upgrades:
- Motor Selection: Choosing a more powerful motor can increase speed and climb rate. Consider the motor’s Kv rating (RPM per volt) and current draw for optimal performance.
- Battery Selection: Upgrading to a higher capacity battery can extend flight time. Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries are popular due to their high energy density.
- Propeller Selection: Selecting a propeller with the appropriate pitch and diameter can optimize thrust and efficiency. Experimenting with different propellers can fine-tune the aircraft’s performance.
Implementing Control Systems
Implementing control systems like flaps, ailerons, and rudders provides greater control over the aircraft’s flight path and maneuvers.
- Flaps: Flaps are movable sections on the trailing edge of the wing that increase lift and reduce stall speed. They are typically deployed during takeoff and landing for greater control and maneuverability.
- Ailerons: Ailerons are control surfaces located on the trailing edge of the wings. They are used to roll the aircraft by deflecting in opposite directions. Ailerons are essential for coordinated turns and maintaining lateral stability.
- Rudder: The rudder is a control surface located on the vertical tail. It is used to yaw the aircraft, changing its direction. The rudder is essential for maintaining directional stability and for ground maneuvers like taxiing.
Integrating Advanced Features, Diy rc airplane
Integrating advanced features like landing gear, camera systems, and autopilot can enhance the functionality and capabilities of your DIY RC airplane.
- Landing Gear: Landing gear allows the aircraft to take off and land on a runway or other surfaces. There are various types of landing gear, including fixed, retractable, and tricycle configurations.
- Camera Systems: Integrating a camera system allows you to capture aerial footage from your RC airplane. This can be achieved using a GoPro or other action cameras, mounted on a stabilized platform to ensure smooth footage.
- Autopilot: An autopilot system can control the aircraft’s flight path autonomously. This allows for hands-free flight, enabling features like waypoint navigation and automatic landing.
DIY RC Airplane Projects and Tutorials

This section provides a collection of DIY RC airplane projects, ranging from simple beginner-friendly designs to more challenging projects for experienced builders. Each project comes with detailed instructions, step-by-step tutorials, and links to online resources for guidance and inspiration.
Beginner-Friendly DIY RC Airplane Projects
These projects are ideal for individuals new to RC airplane building, offering a gentle introduction to the hobby. The designs are typically simple, requiring minimal tools and materials.
- Foam Board Glider: A classic beginner project that involves cutting and assembling a glider from foam board. This project teaches basic aerodynamics and control principles.
YouTube Tutorial: Foam Board Glider - Simple Stick Airplane: This project involves constructing a basic stick airplane with balsa wood and tissue paper. It introduces the fundamentals of airplane construction and flight control.
RC Groups Forum: Simple Stick Airplane Build - Park Flyer: Park flyers are small, lightweight RC airplanes designed for flight in open spaces. These projects often utilize readily available materials like foam board or Depron.
Instructables: DIY Park Flyer
Intermediate DIY RC Airplane Projects
These projects offer a greater challenge, incorporating more complex designs and advanced techniques. They require a basic understanding of RC airplane construction and flight principles.
- Balsa Wood Trainer: Balsa wood trainers are popular choices for learning to fly RC airplanes. These projects involve constructing a sturdy and durable airplane from balsa wood.
RC Universe: Balsa Wood Trainer Build Log - Wing-Span Glider: Wing-span gliders are known for their long wings and excellent gliding capabilities. These projects often involve using balsa wood and a variety of other materials for construction.
YouTube Tutorial: Wing-Span Glider Build - Sport RC Airplane: Sport RC airplanes are designed for recreational flying and offer a balance of performance and ease of handling. These projects typically involve using lightweight materials and incorporating features like flaps and ailerons.
RC Groups Forum: Sport RC Airplane Build
Advanced DIY RC Airplane Projects
These projects are for experienced builders who have a solid understanding of RC airplane design, construction, and flight characteristics. They involve intricate designs, advanced techniques, and specialized materials.
- Scale RC Airplane: Scale RC airplanes are replicas of real-world aircraft, often featuring detailed construction and accurate proportions. These projects require advanced skills in model making, including fiberglassing and painting.
RC Scale Builder: Scale RC Airplane Build Log - 3D RC Airplane: 3D RC airplanes are designed for acrobatic maneuvers, featuring high wing loading and powerful motors. These projects often involve using specialized materials and advanced techniques for construction and flight control.
YouTube Tutorial: 3D RC Airplane Build - Electric Powered RC Airplane: Electric powered RC airplanes are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and environmental friendliness. These projects involve selecting and integrating electric motors, batteries, and electronic speed controllers (ESCs).
RC Groups Forum: Electric Powered RC Airplane Build
The world of DIY RC airplanes is a vibrant and ever-evolving community. With endless possibilities for customization and innovation, the hobby continues to attract enthusiasts of all ages and skill levels. Whether you’re a seasoned pilot or a curious newcomer, building your own RC airplane is a rewarding journey that fosters creativity, technical skills, and a deep appreciation for the art of flight.
Building a DIY RC airplane is a rewarding experience, especially when you see it soar through the air. It requires patience, precision, and a good understanding of aerodynamics. But before you take to the skies, you might want to consider adding a DIY patio screen to your backyard. DIY patio screens can transform your outdoor space into a comfortable oasis, making it the perfect place to relax after a long day of tinkering with your RC airplane.